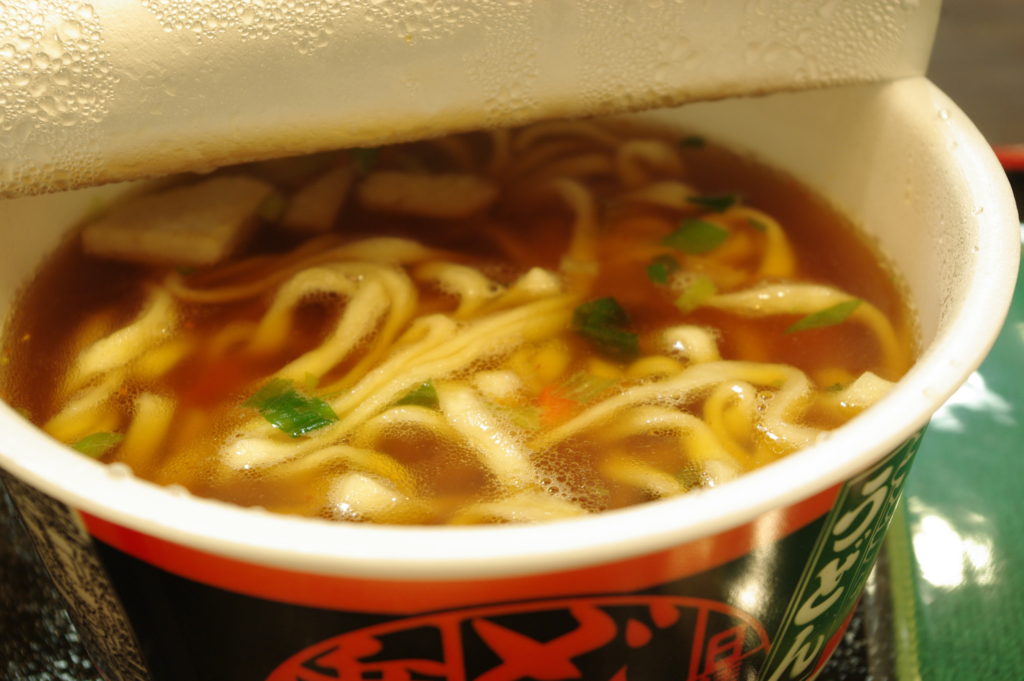
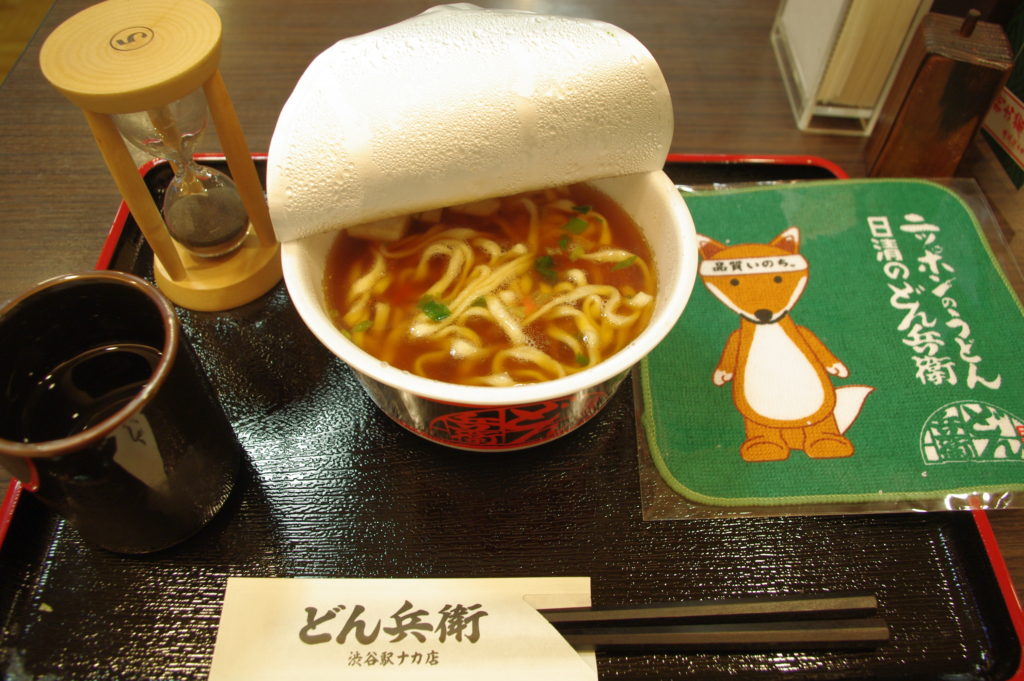
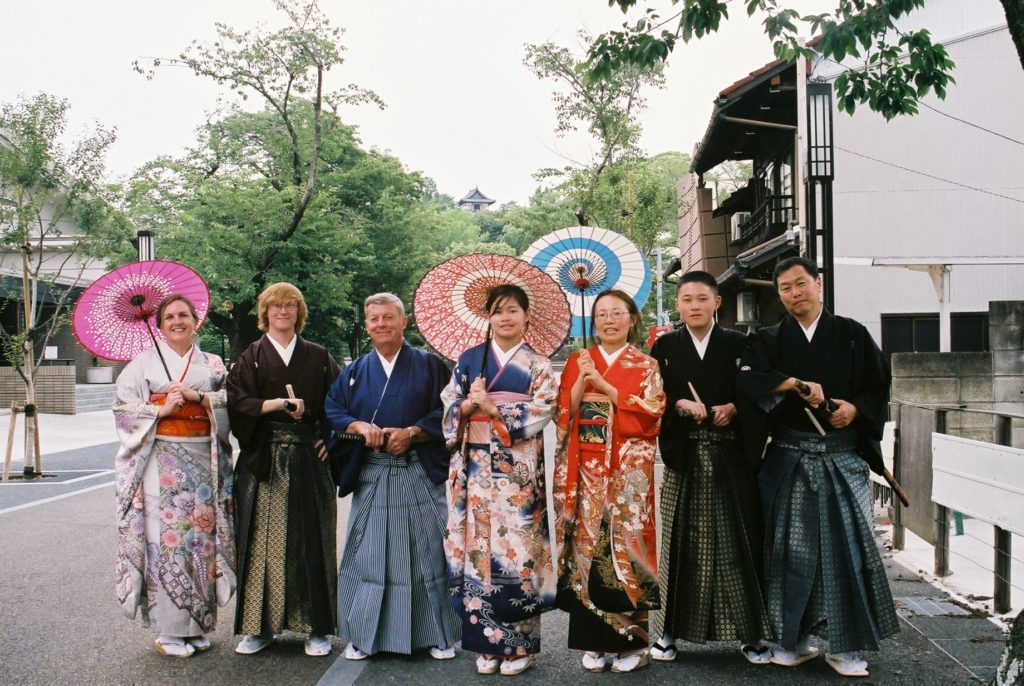
Udon-type wheat noodles topped with a cake of deep-fried bean curd are called kitsune (fox) noodles, so named because foxes are said to like eating deep-fried bean curd. Nissin Foods, famous for having invented instant cup noodles, opened a temporary shop in Tokyo’s Shibuya district where customers can sample instant udon noodles prepared in styles served in different parts of the country for just 200 yen. Since the noodles require about 5 minutes to be completely cooked in boiling water, the set comes served with an hourglass timer. Cup noodles may be one of Japan’s greatest export successes.
Blog News about Japan 未分類
There Is a Reason Why Fugu Is Called a Gun
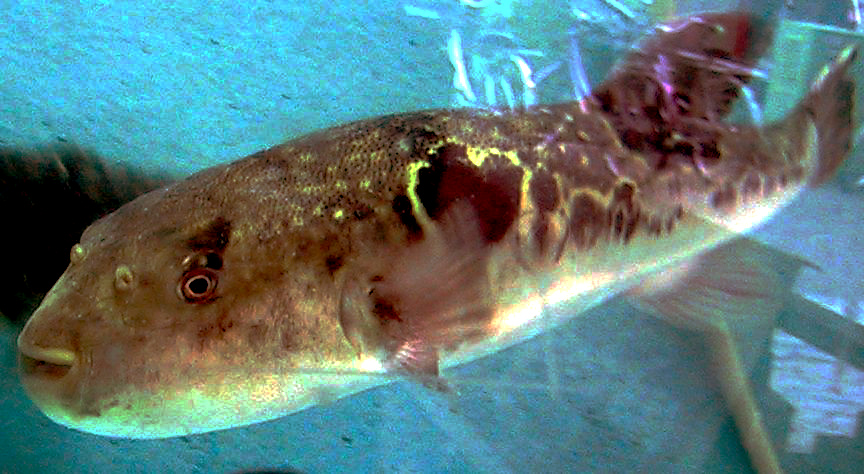

“Shall we go eat fugu (blowfish)?”
If your boss says so and invites you to dinner, and if it’s in Tokyo, you will expect a banquet of “fugu-sashi (fugu sashimi)” or “tetchiri (fugu nabe or hot pot)” while becoming a little nervous imagining what fancy restaurant you will be going to. Fugu has the image of being an expensive food item in Tokyo.
In Osaka, on the other hand, fugu is rather a popular food item that is eaten also at home.
Just go visit a fishmonger to see how popular fugu is in Osaka. Many of the fishmongers in Osaka are licensed to prepare fugu. They clean and cut up fugu by themselves and display them at the front of their shops. The people routinely buy fugu from these shops and enjoy them at home as nabe and other dishes. In fact, Osaka consumes approximately 60% of the fugu sold in Japan. It can be said that Osakans are indeed hardcore fugu fans.
In fugu-loving Osaka, this fish is called “teppo (gun)” or “tetsu” for short. That is, the people liken fugu’s deadly poison to a gun. It suggests that you can die after eating fugu from its poison just like being shot by a gun. The fugu nabe is called “tetchiri (tetsu-chiri; gun hot pot)” while fugu sashimi is called “tessa (tetsu-sa; gun sashimi).” These are frightful names for dishes.
How strong is the fugu poison that is the origin for the fish being called a gun? There are about 25 types of fugu living in the coastal waters around Japan. Among them, the most prestigious fugu is honfugu, which is also called torafugu (tiger blowfish) in Tokyo. Its taste is exceptional, but it is also the most poisonous.
The fugu’s poison is tetrodotoxin. It is a frightful poison that is approximately 13 times stronger than potassium cyanide. It is said that the intake of only around 0.5 to two milligrams of tetrodotoxin can be lethal for humans. In particular, the liver and ovaries contain large amounts of the poison. And because even the blood contains the poison, only specially licensed people can prepare and sell fugu. If by chance someone is hit by the fugu’s poison bullet, the person will have convulsive seizures or become totally paralyzed and even die in the worst case.
Fugu’s poison is thus high-powered. Therefore, please always remember to have professional fugu chefs prepare the fish or purchase it only from licensed fishmongers.
Blog News about Japan 未分類
Hanasaka Jiisan: The Old Man Who Made a Tree Flower

A long, long time ago, in a certain place, there lived an old man. He had a dog named Pochi. One day, Pochi started barking in the garden behind the house, “Woof, woof!” The old man went to see what the matter was. Wherever the dog barked, “Dig here, woof! Dig here, woof!” the old man used his hoe to dig up the garden. To his amazement, piles and piles of small and large gold coins came up out of the ground.
Next door to the old man, there lived a mean old man. The mean old man felt jealous of the first old man, because he had become so rich. “Please lend Pochi to me too!” he begged the good old man. The mean old man took Pochi home and said to him, “Right. Find some small and large gold coins for me as well!” But Pochi remained silent.
“Hurry up and find the money! If you don’t find it, this is what I’ll do to you!” So saying, the mean old man hit Pochi with a pole. Pochi ran away into the field and barked out, “Woof, woof!”
“Oh, so you’ve found some small and large gold coins, haven’t you!”
But when the mean old man dug up the ground at the place where Pochi had barked, all he found was a whole lot of broken tiles and pieces of cracked bowls. The mean old man was so angry at this that he hit Pochi until the poor dog died.
The good old man had no choice but to bury the dead Pochi in the field behind his house. When he did so, a tree sprouted up on Pochi’s grave, and grew tall right before the old man’s eyes.
The good old man cut down the tree and made it into a mortar. When he used the mortar to make mochi rice cakes, a whole lot more small and large gold coins came out of the rice cakes!
The mean old man saw this and came over again to borrow the mortar. But when he made mochi rice cakes in the same mortar, all he got once again was broken tiles and pieces of cracked bowls. The mean old man got very angry and burned the mortar.
The good old man had no choice but to go and collect the ashes from the burned mortar and take them home. After a while, a lord came past. The good old man climbed up a dead cherry tree, and, spreading the ashes from the burned mortar over it, said, “Let’s have flowers grow on this dead tree! Let’s have flowers grow on this dead tree!”
When he did so, the tree, which until then had been dead, burst into blossom with cherry flowers all over the tree. The lord was so pleased that he gave the good old man many rewards.
When the mean old man saw this, he took some ashes that were left over and climbed up the tree. Then, when the lord passed by again, the mean old man spread the ashes on the tree, saying, “Tree, bloom, bloom! If you don’t, I’ll get mad at you!”
But the tree didn’t blossom into flower at all. Moreover, some of the ashes went into the lord’s eye, making him very angry. Then the angry lord arrested the mean old man and put him in prison.
Blog News about Japan 未分類
Japanese Caramel Candy: Caramel Candy Was First Sold to Adults As a Way to Stop Smoking!
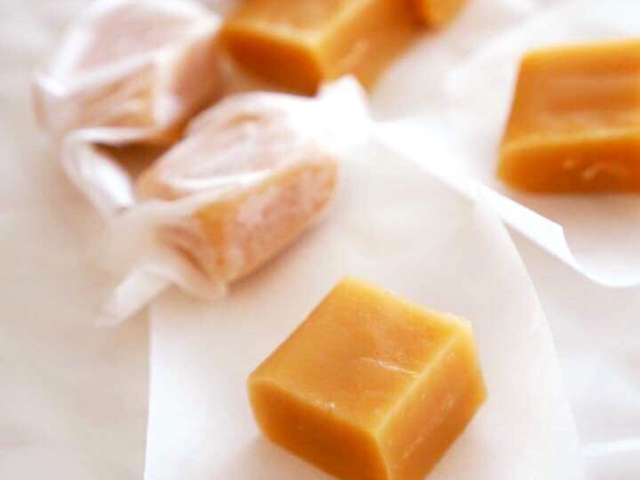

Morinaga Milk Caramel appeared on the market in 1913. This long selling candy has continued to be adored by the Japanese people for nearly a century. Fond childhood memories will surely come to mind to anyone that eats a piece of Morinaga Milk Caramel.
In Japan, the first person to make caramel was Taichiro Morinaga, the founder of Morinaga Confectionery. Taichiro had studied the confectionery art in America. In 1899, Taichiro began making caramel for foreigners living in the Yokohama Foreign Settlement and for Japanese returning home from abroad. It is said that the caramel at that time was rich in flavor with a soft texture because of the large amounts of butter and milk that were used.
Soon after, Taichiro embarked on creating a caramel that would be more suited to the Japanese taste. Taichiro made improvements in the caramel by reducing the amounts of milk and butter used and by making the caramel smaller and a little harder.
When this improved type of caramel was packaged in a small portable box and put on sale at the Taisho Exposition held at Ueno Park in 1914, it proved to be a big hit. Full-scale sales were soon started.
How people originally viewed milk caramel around this time is considerably different from how it is viewed nowadays. It was considered to be a high-class, nutritionally-rich confection ideal for use as a souvenir or present.
There is also a novel poster from that time in which a gentleman is shown to be throwing away his cigarette while holding onto a piece of milk caramel and commenting, “If I can have only one heavenly gift, I’ll choose milk caramel.” Later, a copy with the comment “A substitute for tobacco” was also published.
That is, the milk caramel at that time was a premium confection for adults to be enjoyed by gentlemen and ladies alike. It is a surprise that some people would use milk caramel as a means to stop smoking.
Moreover, there are records showing that milk caramel was supplied to the army for use as an energy supplement for the troops. It is relatively recent that milk caramel has become a children’s candy. Before that, it was a candy for adults.
Blog News about Japan 未分類
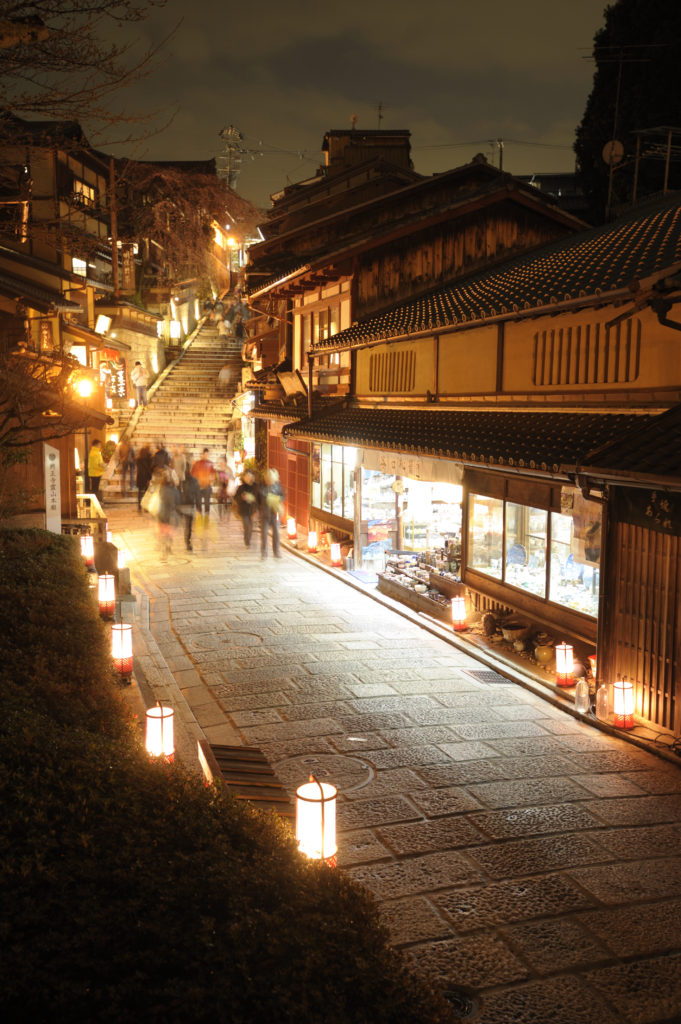
Night Kyoto
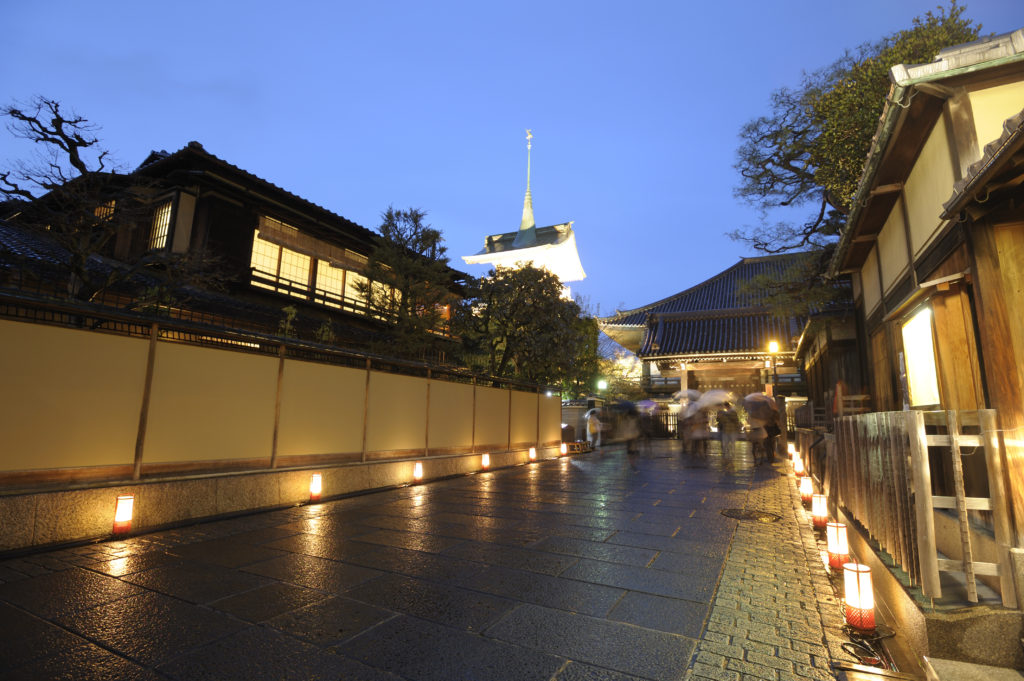

Bringing the city’s streets and alleyways to life with a magical profusion of lights and flowers, it is a seasonal night-time event attended by 2 million people every year.
“Kyoto Hanatouro” was established in March 2003 with the aim of creating a new seasonal event for the 21st Century that would bring color to the Kyoto nightscape. Many of the city’s streets and sites of cultural heritage are adorned with dazzling floral displays and roji andon, square shaped paper lanterns placed to light-up the floor level, which resound with the distinctive character of Japan. The combination of these two decorations lends a truly transcendental appearance to the walkways. Hanatouro’s fame as a romantic event that leaves visitors utterly enraptured by the Kyoto evening-time has spread far and wide, and it attracts over 2 million people every year from both Japan and abroad.
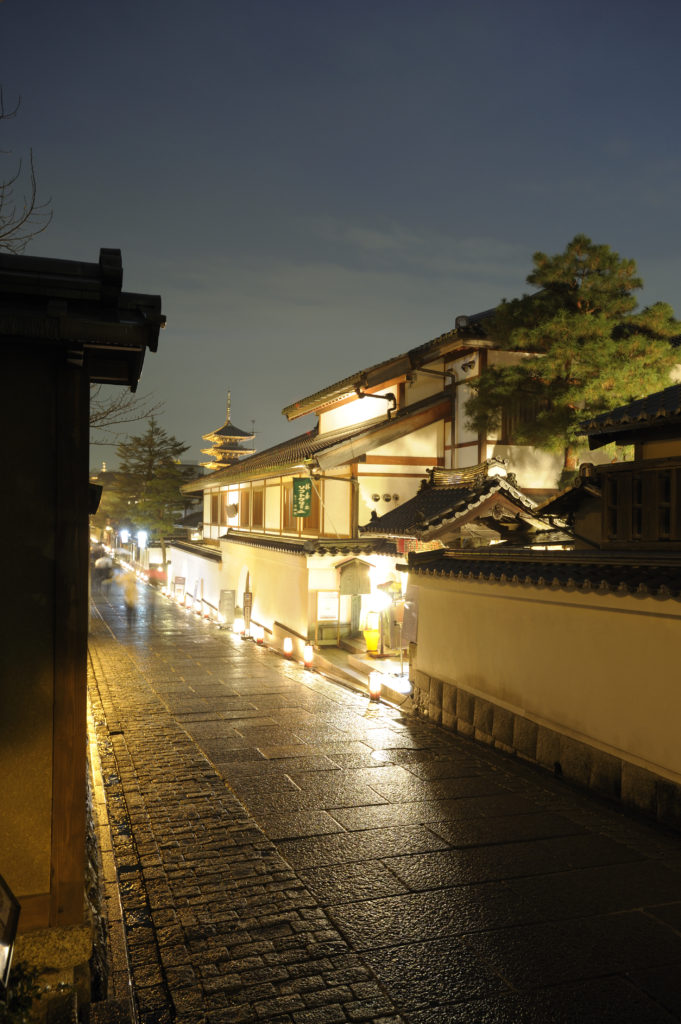

The daylight World Transformed into a Magical Fairy-tale Landscape
Host to the Hanatouro events are the foot of the history-rich Higashiyama mountain, one of Japan’s leading spots of scenic beauty, and. At “Kyoto Higashiyama Hanatouro 2011,” held in March, the walkways of these areas where you can find famous locations are bathed in the gentle glow of over 2,000 andon. The delicate design of the andon themselves demand a second look, each one the product of traditional ceramic and metalwork techniques. Along the way, you will find breathtakingly spectacular floral displays created by professional flower arrangers, adding a dash of magnificent color to the gentle light.
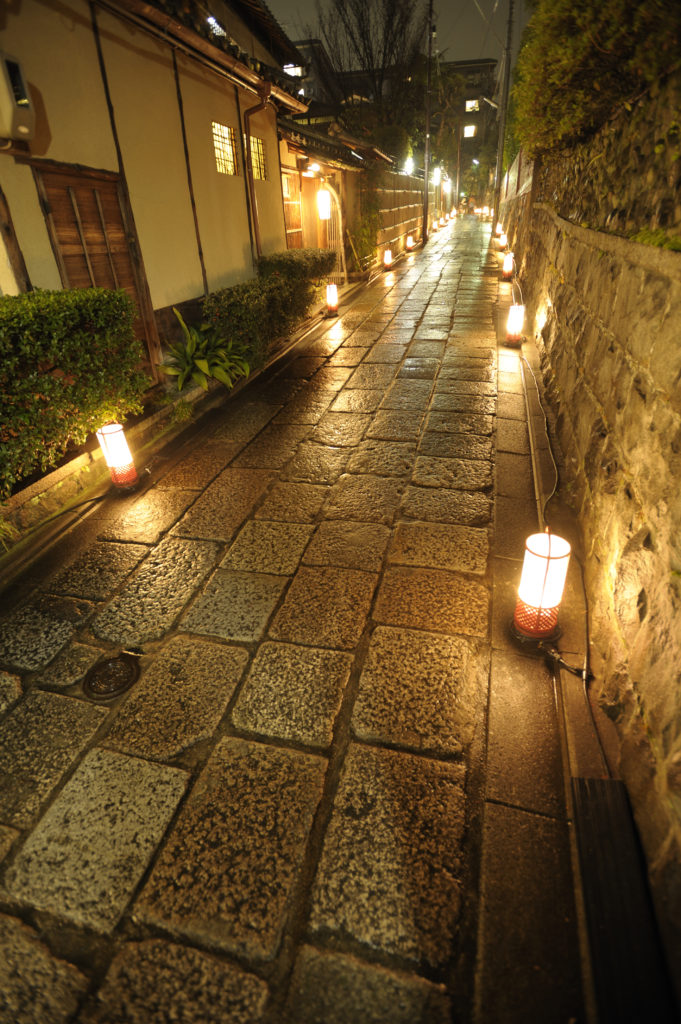

Preparations Also Underway for a Wide Variety of Events Including Illuminations
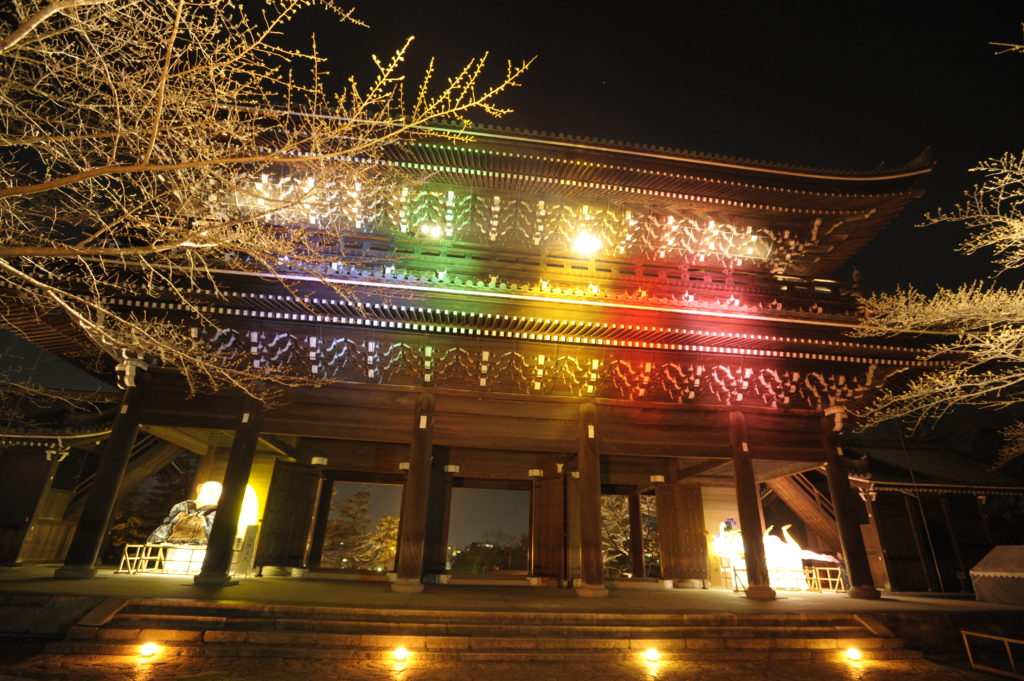
During these events, night-time illuminations are held at famous temples, shrines, and cultural buildings, principally in the areas surrounding the Hanatouro walkways. These locations also hold exclusive public viewings and openings, offering visitors rare opportunities for appreciating traditional Japanese architecture and priceless works of Buddhist art. Furthermore, a wide variety of events are planned to be held, including mini-concerts, and festivities featuring items created around the theme of lanterns.
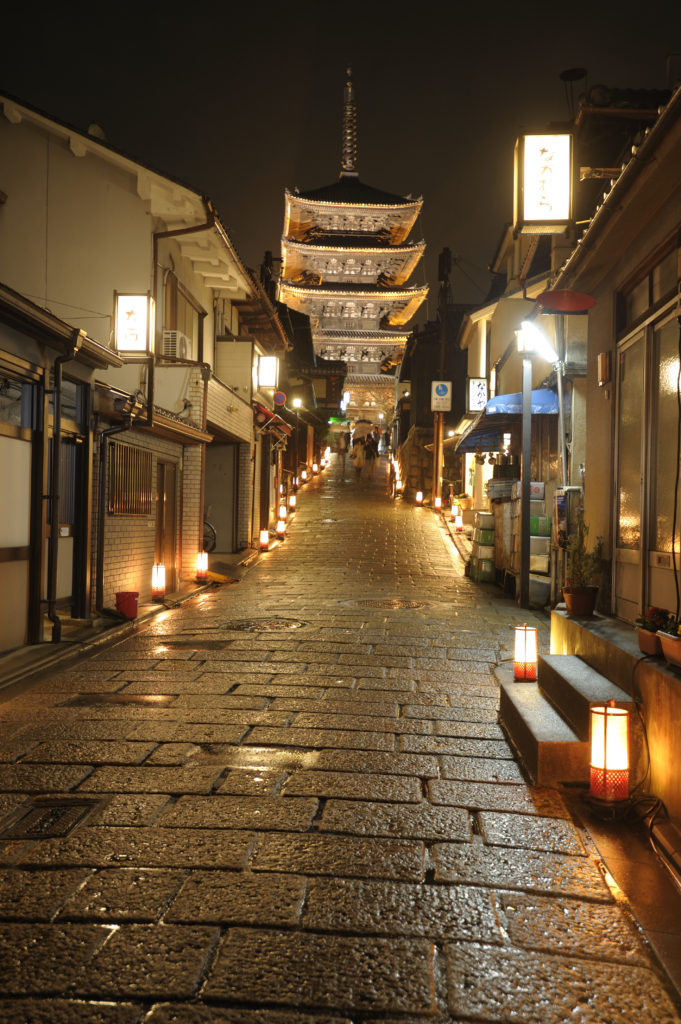

Lanterns and Flower Lane
Approximately
2400 lanterns of six different kinds; Kyo and Kiyomizu ceramics, Kyomei bamboo,
Kitayamasugi round cedar wood, Kyo stone art, the lacquer-coated lanterns and
metal art, decorate the 4.6 km walking path that leads to the foothills of Higashiyama Mountain. From
the north, the path goes through Shoren-in Temple and Maruyama Park, and then
through Yasaka Shrine to Kiyomizu Temple in the
south. Enjoy the striking charms of Kyoto streets:
faint lights that beautify the store fronts of Monzen-machi, soft lights that reflect
off the stone pavements and lights swaying amongst the trees, white and earthen
walls.
The ikebana Promenade and the
abundant ikebana arrangements together with the paper lanterns invite the
visitor to an enchanting world.
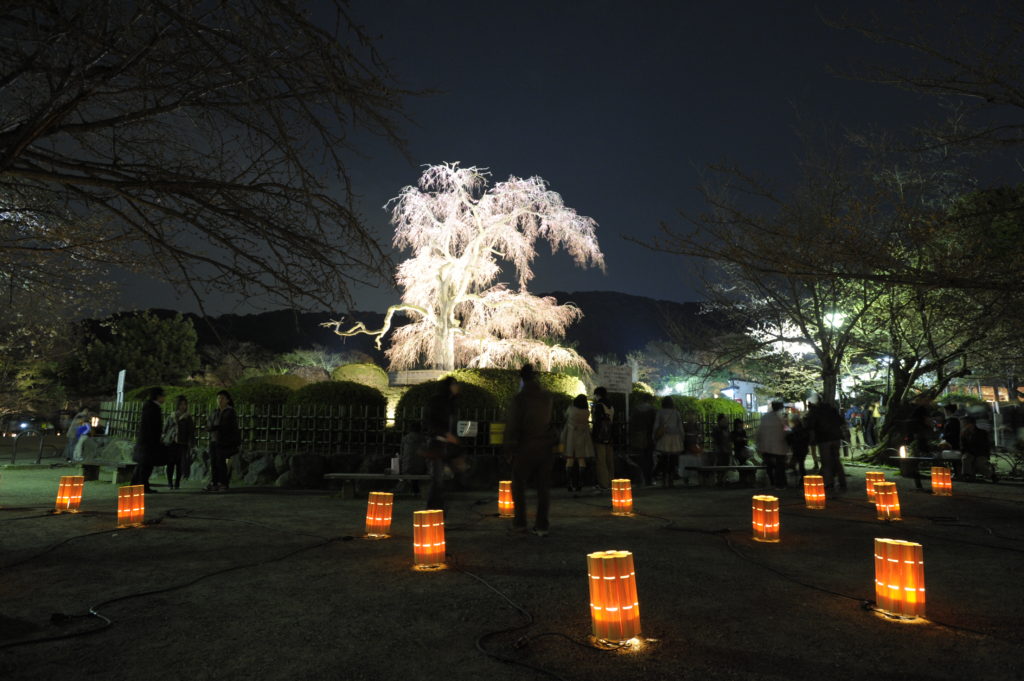

Ikebana Promenade
With
the cooperation of Kyoto Ikebana Association, 10 large flower arrangements are
displayed in the Lanterns and Flower Lane.

Contemporary Ikebana Exhibits
A
grand flower arrangement competition is held with the cooperation of Kyoto
Ikebana Association, in Maruyama Park. 16
flower arrangements are displayed in the early and late stage of the festival.

Big Student Performers Gathering
Student performers from Kyoto and other university towns will be recruited to give street performances at Maruyama Park to provide more color and life to the hanatouro event.
Fire Watch and Ohayashi Music Group

Local school children play wooden clappers, bells and drums and sing children songs about watching the fire and walking through the “Lanterns and Flower Lane.”
Takeakari Yugennokawa (Bamboo Lanterns/Profound Stream)
About a thousand touro lights made of young bamboo are placed on the Yoshimizu Stream and flow through Maruyama Park to create a magical atmosphere
Blog News about Japan 未分類
Momotaro (peach boy)
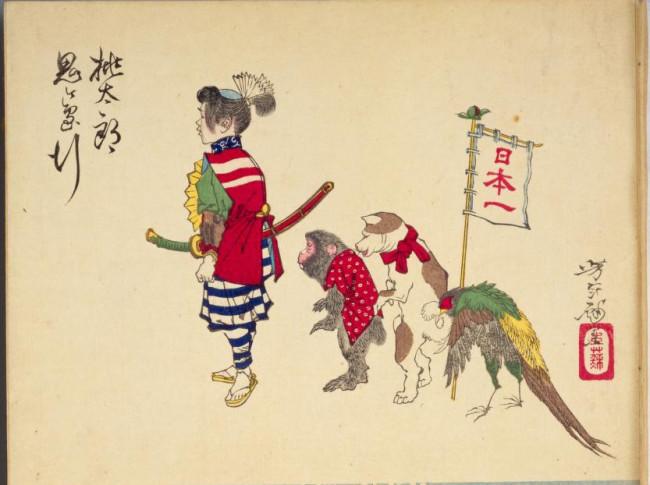

A long time ago, in a certain place, lived an old man and an old woman. The old man went to the mountains to collect sticks for firewood, while the old woman went to do the washing in the river.
While the old woman was doing the washing in the river, a huge peach came tumbling, tumbling, tumbling along in the water. “Oh, this is a nice present to take home!” said the old woman, and picked up the enormous peach and carried it home.
When the old man and the old woman cut open the peach, wanting to eat it, amazingly, a healthy baby boy jumped out from inside the peach!
“This must surely be a gift from God!” The old man and the old woman, who didn’t have any children, were thrilled. They named the boy born from the peach “Momotaro” (meaning “Peach Boy”). Momotaro steadily grew up to become a strong boy.
Then one day he said, “I am going to go to Onigashima (Monster Island) to wipe out the bad monsters.” The old woman made some millet dumplings for him, and then off he went to Monster Island.
Along the way he met a dog. “Momotaro, where are you going?”
“I’m going to Monster Island, to punish the monsters.”
“Well, in that case, please give me one of those millet dumplings around your waist. Then I’ll go with you.” The dog took one of Momotaro’s millet dumplings, and joined him on his travels. Then Momotaro met a monkey. “Momotaro, where are you going?” “I’m going to Monster Island, to punish the monsters.” “Well, in that case, please give me one of those millet dumplings around your waist. Then I’ll go with you.”
After a while Momotaro met a pheasant. “Momotaro, where are you going?” “I’m going to Monster Island, to punish the monsters.” “Well, in that case, please give me one of those millet dumplings around your waist. Then I’ll go with you.”
In this way, Momotaro gained the dog, the monkey, and the pheasant as companions, and they all soon arrived at Monster Island. On Monster Island, the monsters were in the midst of a big drunken party, gloating over all the treasures they’d stolen from villages nearby.
“Let’s get started. Don’t let them get away! Don’t give up! Keep after them!”
The dog bit the monsters’ bottoms, the monkey got on the monsters’ backs, and the pheasant pecked at the monsters’ eyes. All the while, Momotaro fought valiantly, wildly brandishing his sword.
Eventually the chief of the monsters said, “We give up, we give up! You’ve won! Help!” Putting both his hands together in conciliation, he apologized. Momotaro, the dog, the monkey, and the pheasant loaded all the stolen treasures they’d taken from the monsters on to a cart and returned home, in high spirits.
The old man and the old woman were truly delighted to see Momotaro back again, safe and sound. The three lived happily ever after.
Blog News about Japan 未分類
Wailing Over Whaling: Pros and Cons of Whale Hunt in Japan
By Sandra Cave
If Japan’s stolen whale meat scandal in 2008 or the Cove documentary in 2010 on the bloody annual killing of dolphins in Wakayama Prefecture gave you pause to contemplate whaling issues, you would know there are many divergent views on this complex and controversial topic, within, not only between nations, and how important it is to recognize such divergence – to be found among the Japanese people as well.

Japan has been involved in some form of whaling for several hundred years, and before the International Whaling Commission’s (IWC) moratorium to stop commercial whaling came into effect in 1986 (ratified by and binding on Japan) to enable whale stocks to recover from depletion in the 20th century, Japan was heavily engaged in commercial whaling. From 1986, Japan, supported by all major political parties, has continued to hunt whales based on its own catch quotas for research purposes under Article VIII of the International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling (ICRW), giving rise to conflict and argument between pro- and anti-whaling nations, individuals and environmental, animal-rights and other groups.
In 1946 the ICRW, that led to the creation of the IWC, was signed aiming to “provide for the proper conservation of whale stocks and thus make possible the commercial whaling and the orderly development of the whaling industry.”
Because the 1986 moratorium applies only to commercial whaling, whaling under the scientific-research and aboriginal-subsistence provisions of the ICRW is permitted.
Research Whaling
American biologist, J. Smith, longtime resident of Japan with close ties to the Tsukiji fish market in Tokyo, explains, “Japan carries out its whaling in the northwest Pacific Ocean and the Antarctica Ocean hunting primarily the common minke whale and Antarctic minke whale. Though without full consensus, recent surveys estimate a population of 103,000 in the northeast Atlantic, but for Antarctic minke whales, in January 2010, the IWC stated it is unable to provide reliable estimates at present.”
Japan’s research whaling program, conducted by the privately owned and Japan-government funded Institute of Cetacean Research (ICR) is the subject of intense debate. ICR states the four objectives of the research as 1. Estimation of biological parameters to improve the stock management of the Southern Hemisphere minke whale; 2. Examination of the role of whales in the Antarctic marine ecosystem; 3. Examination of the effect of environmental changes on cetaceans; and 4. Examination of the stock structure of the Southern Hemisphere minke whales to improve stock management.
Konomu Kubo, Secretary of the Japan Whaling Association (JWA) said, “The role of JWA is promoting the principle of sustainable use of abundant whale resources and supporting research whaling conducted by the ICR through public relations. We do support the protection of endangered whale species such as blue whales. We are asking for the use of abundant whale species such as minke whales and sei whales.”
Several groups perhaps most famously Greenpeace and the Sea Shepherd Conservation Society contest Japan’s claim of conducting research and say Japanese whaling is a disguise for actually being commercial whaling, and thus a violation or abuse of the 1986 moratorium which Japan agreed to be bound by.
Genevieve Quirk, Greenpeace Whales Campaigner explains, “As an independent organization financially independent from political or commercial interests, our goal is to ensure the ability of the earth to nurture life in all its diversity and we take great care in developing our campaign strategies and policies to reflect our fundamental respect for democratic principles and to seek solutions that will promote global social equity.
Greenpeace is opposed to all commercial whaling in all of the world’s oceans – this has been true for decades and is true today.
This includes Japan’s fraudulent “scientific” whaling carried out in the Southern Ocean, the Pacific and in Japan’s coastal waters. We are completely opposed to all commercial whaling wherever it is carried out and under whatever name.
The Southern Ocean – where Japan’s whaling takes place – was made into a whale sanctuary in 1994, with only Japan voting against it. Since then, Japan’s “researchers” have been gathering data to facilitate increased commercial quotas in an area that has been deemed off limits to commercial whaling.”
Kobu responded, “Article VIII of the ICRW clearly states the right of research whaling by member nations,” that is “… any Contracting Government may grant to any of its nationals a special permit authorizing that national to kill, take and treat whales for purposes of scientific research.”
54-year old IT programs manager Kazunori Inohe notes, “The fact of the sale of whale meat in Japanese shops and restaurants shows there is no truth to the ‘research’ activities and that the killing of whales is obviously for commercial profit.” But for Kobu, “the costs and expenses of the research program are covered by the proceeds from the sale of whale meat and this process is also legal under Article VIII.”
Though the ICR asserts almost half of the IWC members support the sustainable use of whale resources, Greenpeace’s opposition to Japan’s whaling program is largely based on its stance that whales are endangered and so must be protected. For Quirk, “Expectations for the recovery of whale populations have been based on the assumption that, except for commercial whaling, their place in the oceans is as secure as it was a hundred years ago. Sadly, this assumption is no longer valid. This is why we believe that commercial whaling in all forms must be stopped.”
How Many Whales Are Killed?
Arguing that the targeted whale species are too healthy to be harmed, Kubo said, “Under the special permit by the Japanese Government, the recent sampling quotas set by the ICR are 850 minke whales and 50 fin whales at maximum in the Antarctic and 220 minke whales, 100 sei whales, 50 Blyde’s whales and 10 sperm whales in the northwest Pacific Ocean.”
The IWC Scientific Committee has collected up-to-date data on catch limits and catches taken since 1985. Numbers have ranged from less than 200 in 1985 to close to 1,000 in 2007.
Should Lethal Research Methods Be Used?
J. Smith notes, “The need for lethality of Japan’s research whaling is hotly contested and the credibility of the science is questioned. The US, UK and Australia among others say it is unnecessary to kill whales to study them, though ICR asserts that some indispensable data has to be collected by lethal means – such as that relating to ovaries, ear plugs and stomach contents essential for population and ecosystem modeling.”
Greenpeace weighs in, “Japan’s research has been continually dismissed by the International Whaling Commission’s (IWC) scientific committee as “unnecessary”, and was condemned in a resolution passed at the 2007 meeting, when a majority of countries voted for Japan to suspend indefinitely the lethal aspects of its research program.
In an article in the Mainichi Shimbun newspaper in October 2005, Professor Toshio Kasuya of Teikyo University of Science says, “The Institute of Cetacean Research (ICR) argues that lethal research is the only appropriate method to collect the needed data. But examination of biopsy samples reveals the amount of blubber or reproductive rate, and analysis of faces provides information on what whales are eating.
“In reality, of course, the ‘scientific whaling’ program is a way of keeping a foot in the door for Japan, while pushing for a return to commercial whaling at the IWC and actively marketing the ‘byproduct’ of its research – the whale meat at home in Japan. By keeping its whaling fleet functioning, it hopes that, sometime in the future, commercial whaling will resume. Greenpeace pledges to ensure this doesn’t occur.”
Quirk says Greenpeace believes whales do not need to be killed in order to be studied, “Whale scientists all over the world study whales without killing or injuring them. Meanwhile, the JARPA (Japanese) ‘researchers’ insist on using lethal methods not because they are necessary but because they supply whale meat to the markets in Japan and offer an opportunity to train new crew, thus keeping the whaling industry alive.
“Non-lethal methods have huge advantages over lethal ones because they permit repeated observations of the same individual. Lethal methods, by their nature, offer only a snapshot. Once a whale is ‘observed,’ it cannot be observed again later. This makes lethal methods particularly unsuitable for the studies of whale behavior, such as migration, which is of great interest to scientists.”
J. Smith adds, “The Japanese, like the Inuits in Greenland, Norwegians, and New England Americans (among others) have a long, cherished tradition of whaling to supply their vital needs. Other whaling countries include Norway, Russia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, 2 small whaling communities in Indonesia, and natives of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines. Traditionally, whale meat was a staple, and whale blubber and oil, a vital heating source. After WWII, whale oil was also used as an important additive to fortify milk with Vitamin D. When I came to Japan in 1970, kujiradon (grilled whale meat on a bed of rice) was still a staple of students as it was very cheap (about 150 yen per bowl as a lunch special). Today, the meat from ‘research’ whales finds its way to Tsukiji fish market and mostly a few kujira (whale) restaurants in the Kanto area. Many right-wing Diet members strongly favor continued whaling, although the average Japanese could not care less. Surely whale meat is no longer a vital resource, but traditions die hard.”
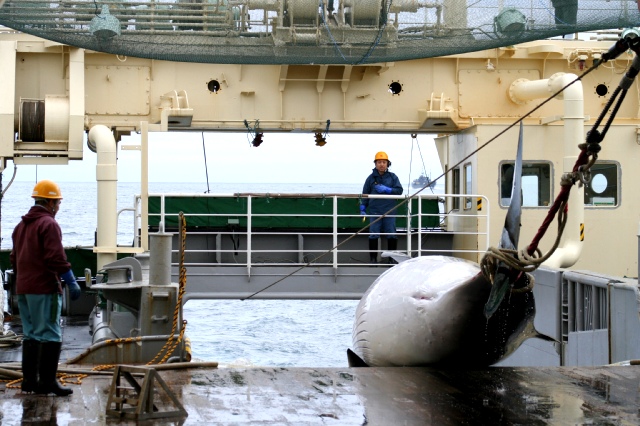

New Zealand, the United Kingdom and Australia are among those countries staunchly opposing Japan’s interest in resuming commercial whaling for reasons including that whaling involves unacceptable cruelty, is not based on genuine needs, and the necessity to conserve endangered species.
But Toshi Ito, 29-year old Tokyo dentist originally from Osaka argues, “Although I heard about the admittedly gruesome sounding method that whales are killed by having a grenade-tipped harpoon into them with the grenade exploding into the whale’s body and that if the whale is not instantly killed a second harpoon may be used or the whale may be shot with a rifle until dead, people should remember that the killing of foxes and other domestic animals often takes longer, as can the killing of animals on safari, and that some animals like ducks are killed for sport – so how can these acts be said to be more humane?”
Is Whale Meat Safe to Eat?
Quirk warns, “If you’re thinking of eating whale, you might want to think again – the blubber of dead whales in some areas is so highly contaminated with organochlorines such as PCBs and pesticides that it would be classified as toxic waste!
“Dr. Yosuke Seki, bariatric (weight-loss) surgeon at Yotsuya Medical Cube, Tokyo, adds, “Some point out that whale meat may contain high concentrations of toxic substances such as mercury, PCB etc., because whales are at the top of the food chain in the sea, but as to the separate matter of its nutritional status, whale meat is very high in protein and very low in saturated fat.
“The whaling issue is very controversial and covers various aspects such as nutrition, environment, food, culture, money, politics, perhaps even religion, among others and these multiple factors make the related issues very difficult to solve.
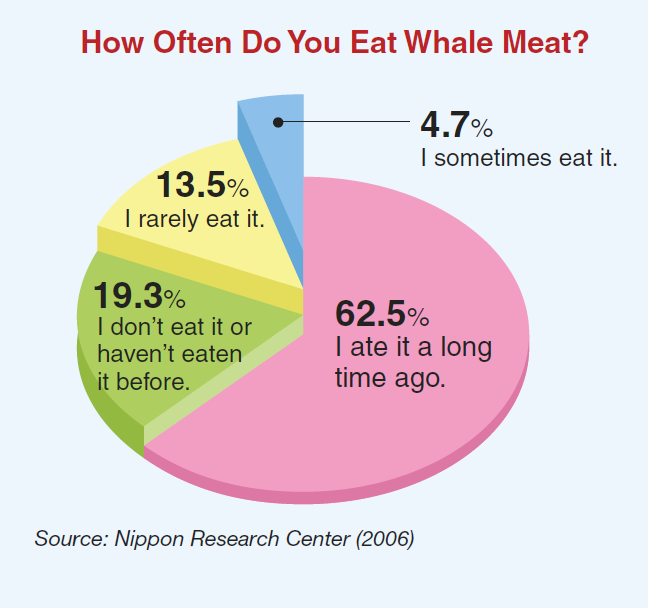
“Different people in different parts of the world have different opinions. To me, it seems almost impossible to make any judgment on this. Maybe I can say that the current impact of whale meat on the general Japanese nutritional status would be practically naught because we very rarely eat it nowadays — though around 30 years ago, it was still eaten in homes and as a school lunch.
“It would be very difficult to draw any conclusion on this issue at the moment and if we really want to do that, I think we definitely need more objective, neutral and scientific evidence. Otherwise this problem will never be finally sorted out. I know Japan and Australia, which is one of my very favorite countries, argue about whaling – I’m sincerely hoping and do believe that Japan and Australia will always remain the very good friends that we are.”
What Is the Fuss About?
Miyuki
Nomura, a 39-year old mother and bank employee doesn’t understand the fuss made
over whaling, “I don’t understand why whaling causes so many disputes in the
world. As Japanese, I feel that Sea
Shepherd and some of the other environmental protection groups are being too
radical about all this.
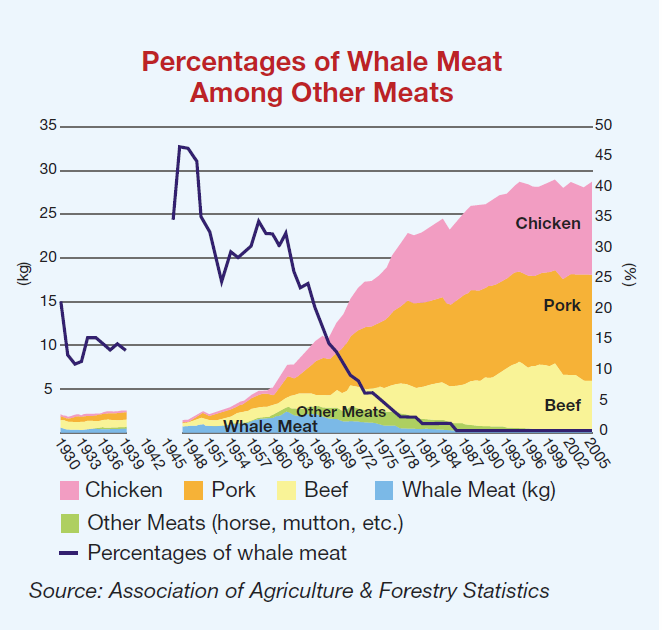
“In Japan after WWII, Japan
was still economically poor, so a single whale could provide a huge amount of
inexpensive meat, in fact over 50% of the meat eaten in Japan at that
time. Japanese in their late 40s or
older ate whale as “school
lunch.” Need for whale meat decreased as other types
of meat got more popular in the 1970s – when whale meat was taken off school
menus.”
It has made a recent comeback though – Japan has started to serve whale meat in school lunches as part of a government initiative to reduce the amount of some 5,000 tons of stockpiled whale meat. For Ruth Nakamura of Tokyo, “I am not thrilled about whale meat being fed to school children, but focusing on that issue seems to be missing the broader scope of things – that the IWC is just a front for the Japan Whalers Association, not really interested in the science of declining whale populations or any ethical perspectives. So Japan is allowed by the IWC to whale “for research purposes?” How absurd! If there was an international body dedicated to actually monitoring the threatened species and making policy, and if that body said to Japan, OK, you can carry on your centuries-old tradition in this manner, e.g., for this period, taking only this number of this type of animal, then I would have no problem with whaling. But calling it ‘research’ is just a crock of bull!”
Miyuki continued, “I imagine that it would be a great experience to see whales swim beautifully in the oceans, but I do not think whales should be protected unconditionally. There is too much heated politics and emotion factoring into this debate just because Japan and some Western countries have different attitudes toward whaling – this is probably because they have made different uses of whales: Japan as ‘food’ and Western countries as ‘oil’ or ‘fashion’ (women’s corsets).”
Australian mother of 3 and correctional officer, 47-year old Sandhra Sullivan says, “I feel angry when whalers go into prohibited areas near Australia and Antarctica to catch whales. It is also not humane how they kill them. They are wiping out the whale population and why do they still hunt whales when nearly every other country is against this practice to help save the whales?”
Policy analyst Bel Braithwaite in Tasmania echoes similar sentiment, “I am personally totally against whaling. I find the whole whaling-fishing abhorrent and support the anti-whaling protests. You would find that a lot of people in Australia are against whaling. A few weeks ago, a whale and its calf were seen in the Derwent River and it drew a huge crowd of people to see them. It was beautiful to watch.”
But many non-Japanese support Japan’s whaling position. Max Cartwright, a London-born 31-year old
systems analyst says, “I feel that it’s
hypocritical to say that eating pork or beef is fine but whale meat is not
fine. How can some people think that
whales are far more intelligent/emotional animals compared to cows or
pigs? Why is there no such vocal
opposition to other people (countries) eating dogs or horses? Why is the supposed intelligence of whales a
determinative factor in the first place?
Is that to say it would be more ‘ethically acceptable’
to kill ‘dumb’ animals? It is possible
that over-protection of whales could cause harm to the food chain, if whale
numbers increase too much and so become detrimental to other marine animals in
terms of their feeding needs.”
Miyuki added, “But probably in 20 years or so, the younger generations in Japan
will be less interested in whale meat – it really isn’t that important these
days as a food source considering what is actually far more popularly eaten in
Japan, such as fish, pork, beef and chicken.”
Yoko Morioka, 40-year old mum of 3 children in Saitama Prefecture together with her Canadian husband Jack feel that, “Other countries have no right imposing their different ethical, moral or cultural values on Japanese as long as whales are used according to international law and science. We must respect each other’s different views, and Japan should not be forced to change its position. The world is not against Japan, it’s mainly Western rich countries pumped up by the media and exploited by anti-whaling fundraising NGOs.” Kubo adds, “I believe that those groups are collecting a lot of donations by spreading misinformation.”
Mariko Sasaki, medical researcher at a medical university in Tokyo, strongly opposes whaling, “Many Japanese are against whaling, and whaling is a very serious issue for me. My major at university was zoology and so I’ve been always interested in conservation of wildlife. I’ve talked about this issue often with Japanese friends and know most ordinary Japanese citizens are against whaling.
“It’s more than obvious that objective research shows some whale species are getting to be in danger of extinction. But I’ve heard that sometimes even scientific research data has been manipulated by some politicians who received benefits from whaling groups. Japanese whaling is protected for only those whaling groups and people who gain from whaling. I strongly disagree with even so-called “research whaling” because Japan’s research whaling is just a cover for commercial hunting.”
For Quirk as regards future whale populations, “Whaling is no longer the only threat to whales. The oceans, or rather, human impacts on the oceans, have changed dramatically over the half-century since whales have been protected. Known environmental threats to whales include global warming, pollution, overfishing, ozone depletion, noise such as sonar weaponry, and ship strikes. Industrial fishing threatens the food supply of whales and also puts whales at risk of entanglement in fishing gear.”
J. Smith added, “IWC has noted that the research results could potentially allow for an increase in the number of minke whales annually taken, though blue whale populations have declined sharply thus putting them at risk of extinction. Other whale species, in particular the minke whale have never been considered endangered.”
At
the June 2010 IWC meeting the 88 member nations decided to postpone a decision
on a 10-year compromise proposal to lift the 1986 moratorium banning commercial
whaling, and to have a one-year cooling
off period before recommencing discussions.
Kubo
would like people to understand that, “Japan is a highly responsible country in
the international society. We do not
mean to overexploit whale resources, but we want to utilize only a part of
abundant whale resources and maintain our whale diet culture into the
future. Different
groups of people have their own food cultures all over the world, and we all
should recognize each other’s — otherwise, wars will
not disappear in the world.”
Blog News about Japan 未分類
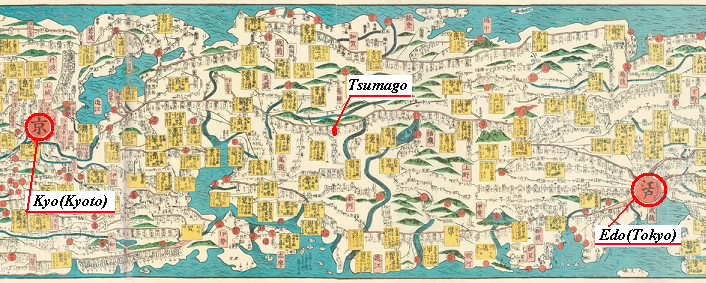
Exploring “Nakasendo”
What is NAKASENDO?
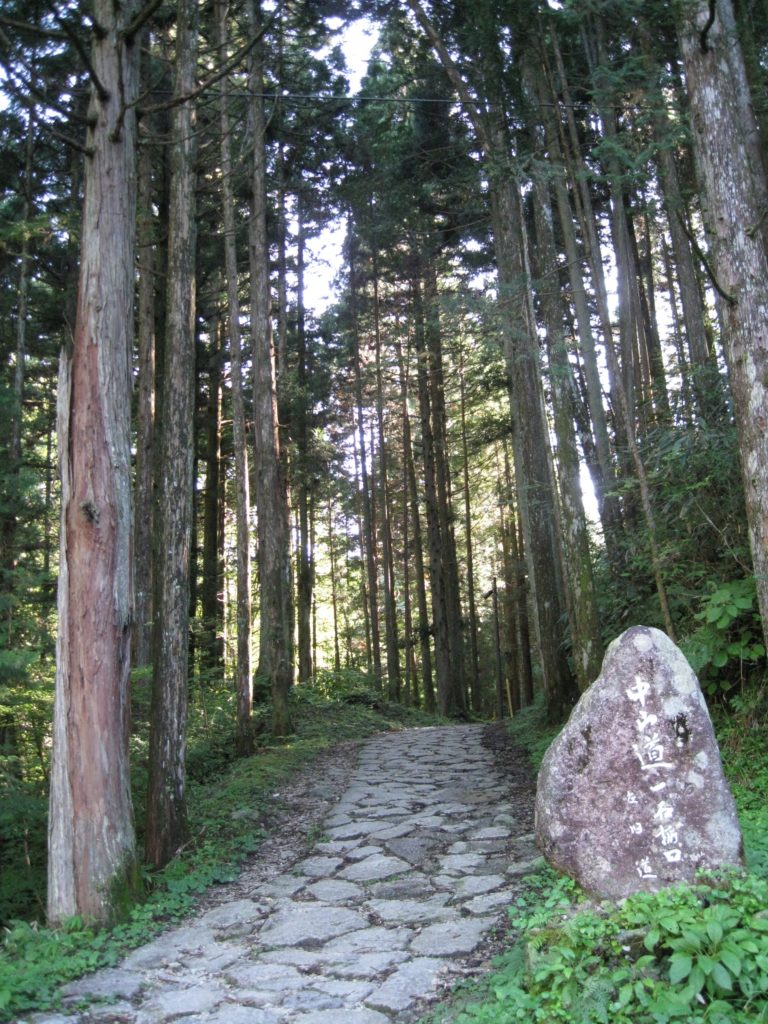
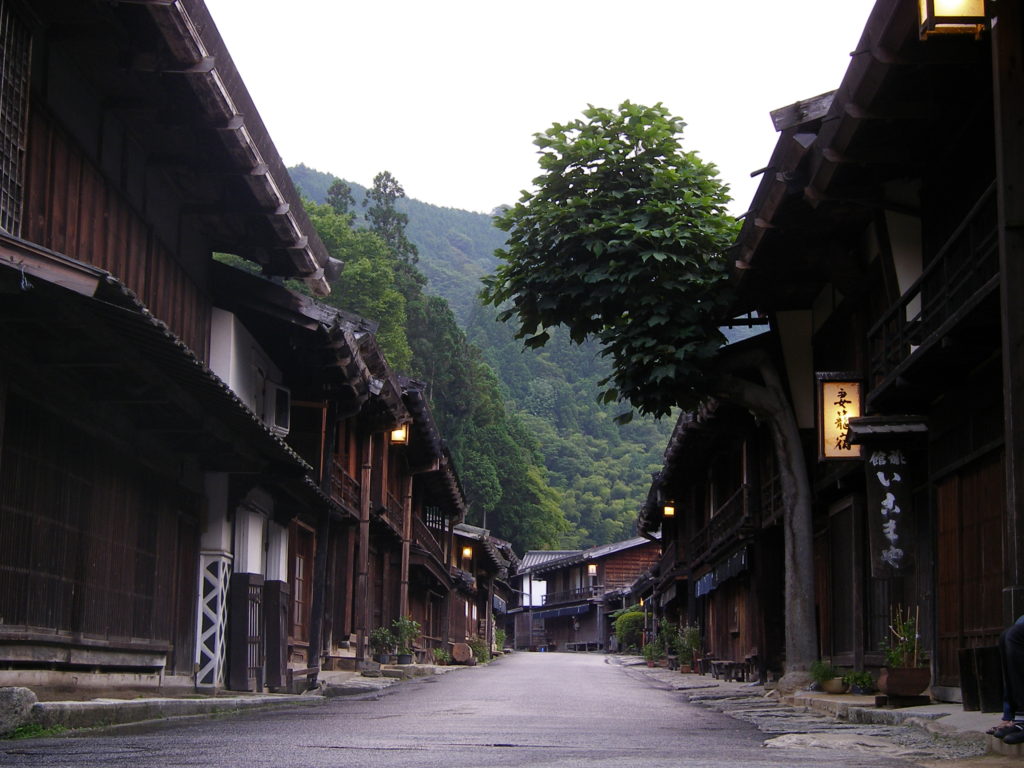
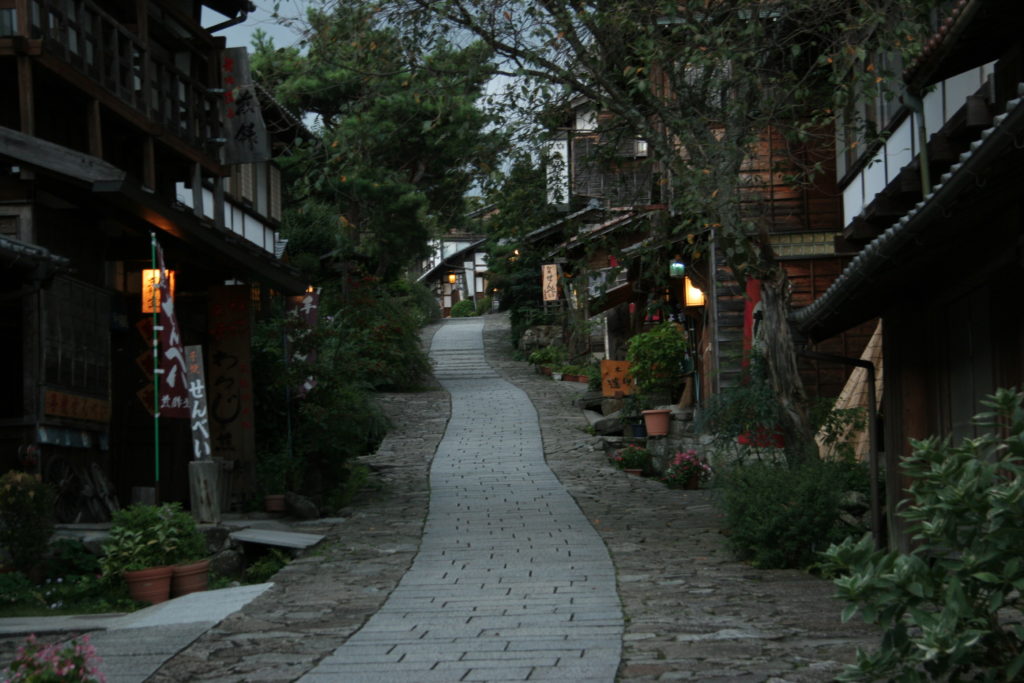
The Nakasendo was one of the five routes of the Edo period, and one of the two that connected Edo (modern-day Tokyo) to Kyoto. Kisoji is a mountainous region along the route in Nagano Prefecture. Travelling in the Kisoji region is a trip back in time to sleepy post towns of the last century. Tsumago and Magome are wonderful places for a short escape from modern life. Without the power lines and concrete buildings that spoil so many historical sites in Japan, Kisoji is a world of old Japanese inns, delightful mountain views, bamboo forests, rambling brooks turning water wheels, looms and lanterns, and beautiful handicrafts.
If you would like to do some hiking, see some incredible architecture, stay in a very traditional Japanese inn, and see what an old post town was like, a trip to Kisoji will be one of your most memorable Japanese holidays.
TSUMAGO VILLAGE
Tsumago was a post town on the Nakasendo route between Kyoto and Edo. It is known today as one of the best preserved post towns in Japan. The town and its residents go to great lengths to recreate the ambiance of the Edo Period. Cars are prohibited on the main street in the day and phone lines and power cables are kept concealed, allowing visitors to imagine they have slipped back to an earlier time.
What is WAKIHONJIN?
In contrast to the honjin (the Japanese word for an inn for government officials), the antiquity of the wakihonjin (smaller honjin) is entirely genuine; the building dates back to the 19th century. It now serves as a museum, and tours are held in Japanese.
MAGOME VILLAGE
The town has been beautifully restored with a broad stone walkway lined with carefully tended foliage. Magome’s embellished preservation contrasts with the rugged authenticity of neighboring Tsumago. The two towns are connected by the Magome-Tsumago Trail, a route which was part of the Nakasendo.
Blog News about Japan 未分類
Inuyama Area in Japan
Inuyama is a city located near Nagoya in Aichi Prefecture. There are a number of famous attractions in the city, based on rich nature, history, and culture. Designated as a Japanese national treasure – Inuyama Castle, the tranquility of a tea garden, and traditional Cormorant Night Fishing are famous even outside of Japan. The history of the town goes back to the ancient Tumulus period. You can feel the long history once you are in the town and time goes by so slowly.
《National Treasure Inuyama Castle》
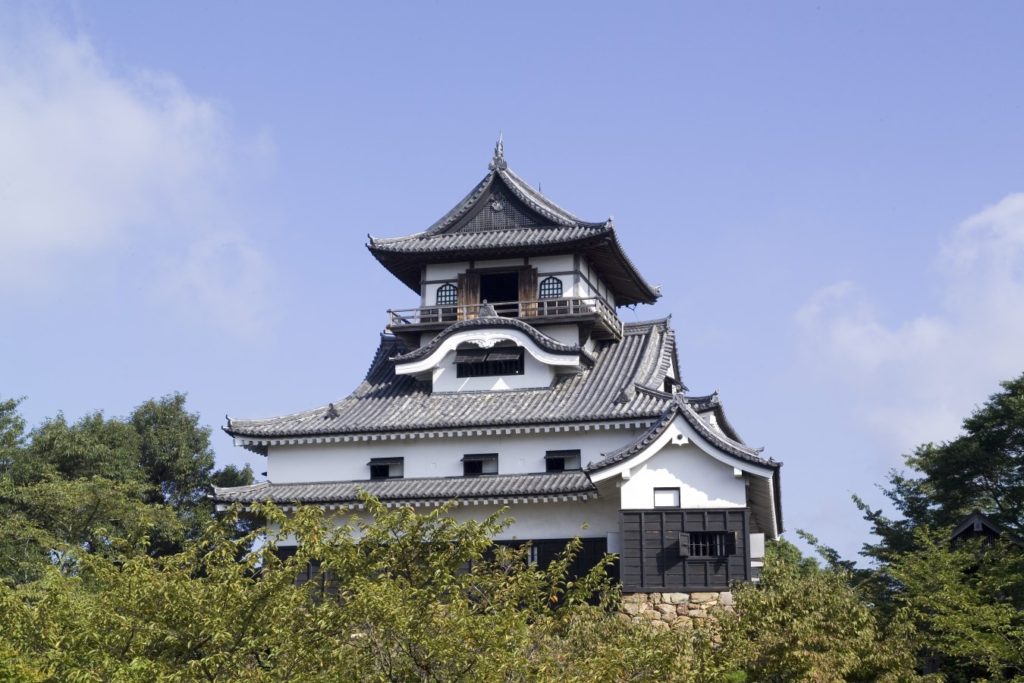

Lying on the southern riverbank of the Kiso river, Inuyama Castle and its donjon were completed in 1537, by Oda Nobuyasu who was an uncle of Oda Nobunaga, the great warlord. It is said to have the oldest remaining donjon in Japan earning it national treasure status. It is a four-story structure with two underground levels. Built on a 40m rise overlooking the river, the top floor is an excellent observatory with a wonderful view.
《Koheji》
The trend to wear the casual kimono called yukata in summer has been revived, and increasingly young people go to festivals wearing yukata. A yukata is an informal unlined summer kimono usually made of cotton, linen, or hemp. Yukata are most often worn to outdoor festivals, by men and women of all ages. Kohiji is a training school to learn how to wear kimono. Participants can wear yukata or kimono with professional guidance.
《National Treasure Tea House “Jo-an”》

Another famous attraction is the Uraku-en tea garden used for tea ceremonies. This garden contains the Joan tea house, built by Oda Uraku, younger brother of Oda Nobunaga. He was a student of the famous tea master Sen no Rikyu. While the Joan tea house was originally built in Kyoto, it was moved to its current location in 1972 though already registered as a national treasure in 1951, one of only three tea houses of its kind. The building is considered one of the finest examples of tea house architecture.
《Cormorant Fishing in the Kiso river》
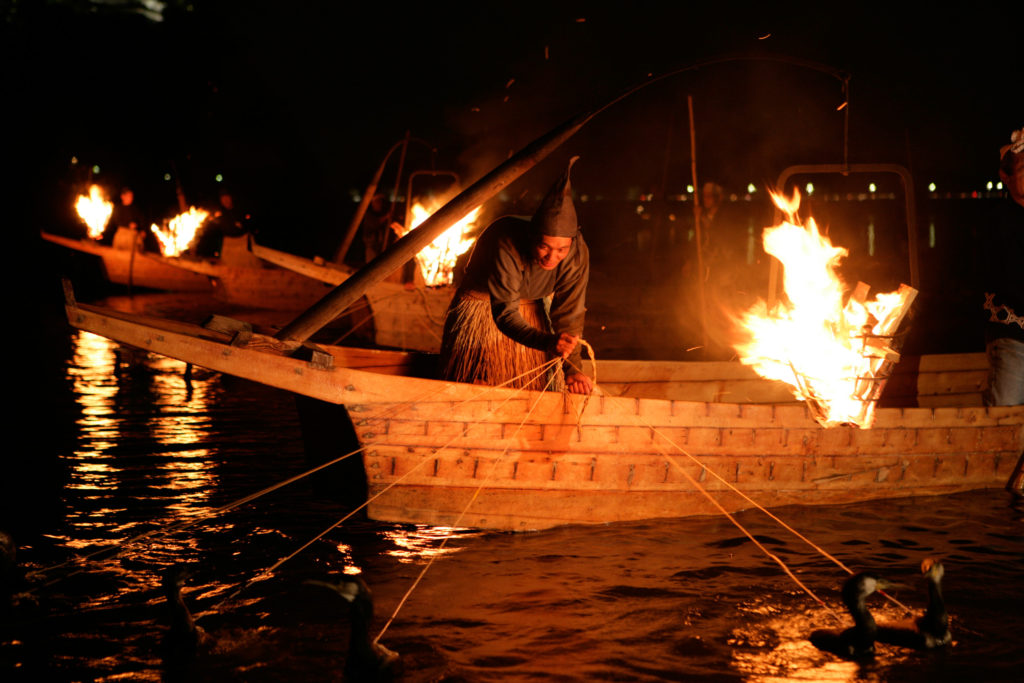

Cormorant fishing is a traditional fishing method in which fishermen use trained cormorants to fish in rivers. Cormorant fishing in the Kiso river has a long tradition. Actually Nagara river is the most famous for this method of fishing which has continued uninterrupted for the past 1,300 years. With the evening sky and the imposing sight of Inuyama Castle as a backdrop, boats glide down the Kiso river, their fishing lanterns reflecting in the river’s dark surface. Each fisherman handles a few cormorants, controlling them with strings. Dressed in a traditional straw raincoat, he conjures up an image from a classical Japanese picture scroll.
未分類
Sawayama Castle
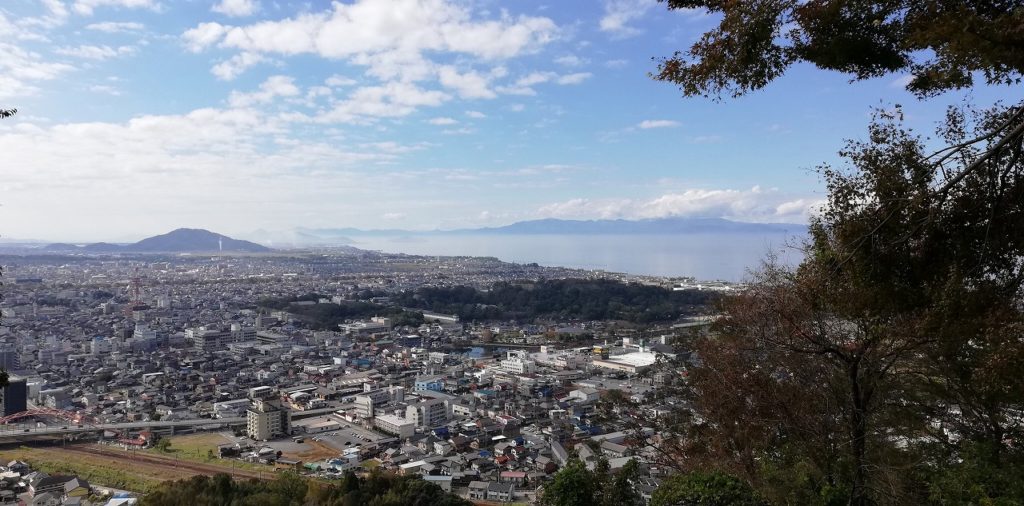

Sawayama-jo Castle was located on a mountain overlooking Lake Biwa. It is famous as the castle of Mitsunari Ishida, a busho (Japanese military commander) in the Sengoku period. The mountain is about 150 meters high, so it’s perfect for hiking.